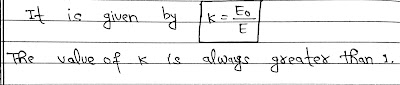Chapter-2|Electrostatic Potential and Capacitance| NCERT 12th Physics:
Dielectrics and Polarisation:
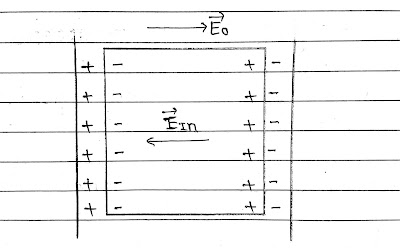
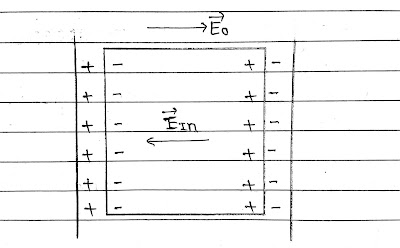
In a dielectric under the effect of an external field, a net dipole moment is induced in the dielectric due to molecular dipole moment, a net charge appears on the surface of the dielectric.
These induced charges produce a field opposing the external field. Induced field is lesser in magnitude than the external field. So field inside the dielectric gets reduced.
Dielectric Constant (K):
The ratio of the strength of the applied electric field to the strength of the reduced value of the electric field on placing the dielectric between the plates of a capacitor is called the dielectric constant of the dielectric medium.
Polarisation (P):
The induced dipole moment developed per unit volume in a dielectric slab on placing it in an electric field is called polarization.
If P is induced dipole moment required by a atom of the dielectric and N is the number of atoms per unit volume, then polarization is given by
P = Np
The induced dipole moment acquired by atom is found to be directly proportional to the reduced value of electric field and is given by
P =α ε₀E
Where α is called constant of proportionality and is called atomic polarisability.
Electric susceptibility (χ):
The polarization density of a dielectric slab is directly proportional to the reduced value of the electric field and it is given by
Dielectric Strength:
The maximum electric field that a dielectric can with stand without breakdown is called its dielectric strength.
For air it is about 3×10⁶ V/m.