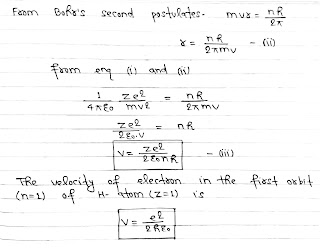
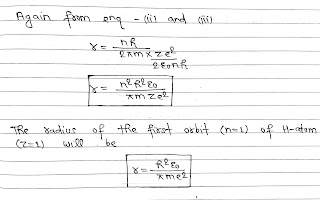
According to Bohr’s theory, A hydrogen atom consists of a nucleus with a positive charge Ze and a single electron of charge e⁻, which revolves around it in a circular orbit of radius r. Here Z is the atomic number and for hydrogen Z= 1.
The electrostatic force of attraction between the nucleus and the electron(e⁻) is
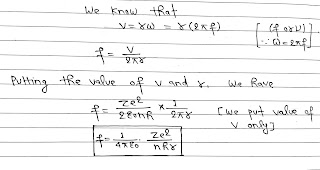
Frequency of Electron in Stationary Orbit:
It is number of revolutions completed per second by the electron in a stationary orbit, around the nucleus.