Position Vector
A vector that extends from a reference point to the point at which particle is located is called position vector.
Let r be the position vector of a particle P located in a plane with reference to the origin O in x-y plane.

Displacement Vector
Displacement vector is that vector which tells how much and in which direction an object has changed its position in a given time interval.
Let an object moving in the x-y plane. Let it is at point P at any instant t₁ and at point Q at any later time t₂.

In ∆OPQ,
OP + PQ = OQ
PQ = OQ – OP
∆r = r₂ – r₁
If the position coordinate of point P and Q are (x₁, y₁) and (x₂, y₂) respectively, then
r₁ = x₁ i^ + y₁ j^
r₂ = x₂ i^ + y₂ j^
Displacement Vector ∆r = r₂ – r₁
∆r = (x₂ – x₁)i^ + (y₂ – y₁) j^
For Three Dimensions
∆r = (x₂ – x₁)i^ + (y₂ – y₁) j^ + (z₂ – z₁)k^
Velocity Vector
The rate of change of displacement of an object in a particular direction is called its velocity.
It is of two types.
(I) Average Velocity
It is defined as the ratio of the displacement and the corresponding time interval.
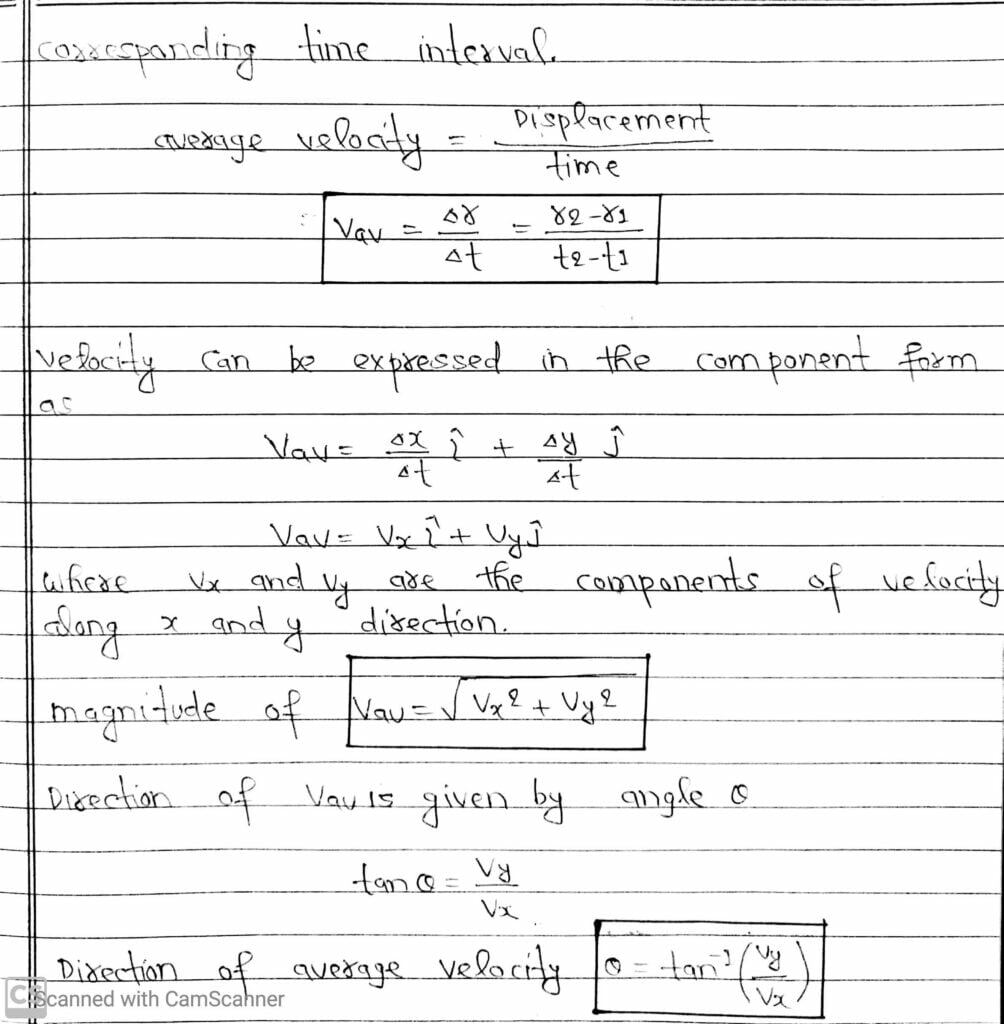
(II) Instantaneous Velocity
The velocity at an instant of time t is known as instantaneous velocity.
The average velocity will become instantaneous, if ∆t approaches to zero.
The instantaneous velocity is expressed as-
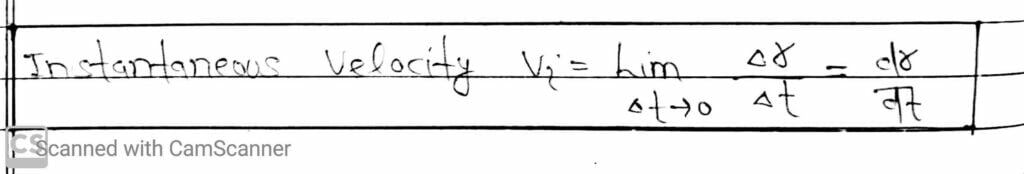
NCERT Class 11 Physics Book PDF Free Download
Also Read
SL Arora Class 11 Physics Book PDF Free Download
All In One Arihant Class 11 Physics Book PDF Free Download
Arihant All In One Chemistry Class 11 Book PDF Free Download
NCERT Class 11 Physics Hand Written Notes Chapter-Wise
Chapter-1(Physical World) PDF Free Download
Chapter-2(Units and Measurement) PDF Free Download
