We assume the earth to be a homogeneous sphere. Let ρ be the mean density of the earth and a body be lying on the surface of the Earth, where the value of the acceleration due to gravity is g.

Now, the body be taken to a depth d below the free surface of the Earth, where the acceleration due to gravity is gd. Here, the force of gravity acting on the body is only due to the inner solid sphere of radius (R – d).
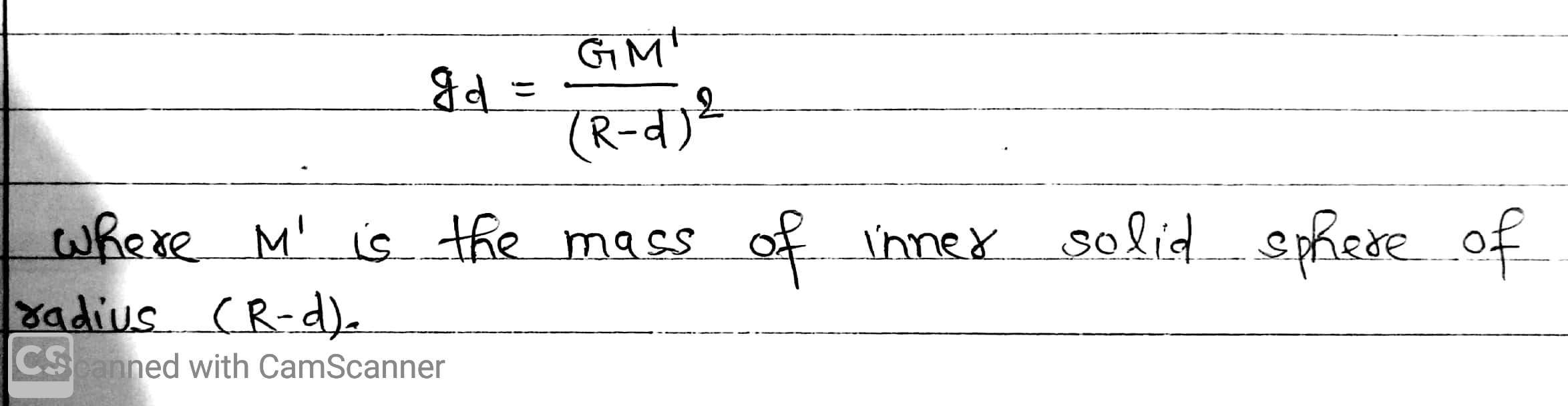
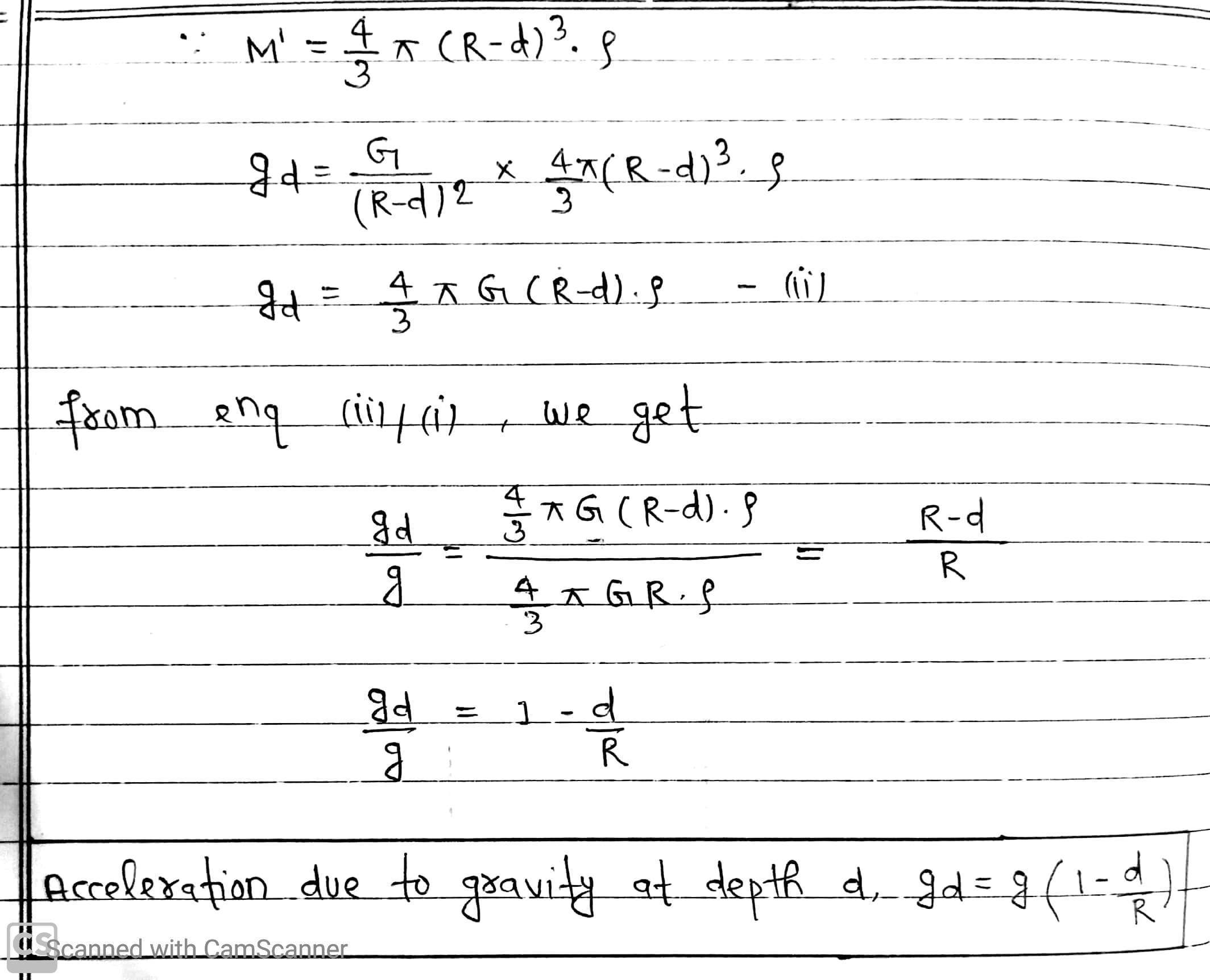

From above it is clear that if d increases, gd must decreases, because g is constant.
Hence, the acceleration due to gravity decreases as we move down into the surface of the earth.
