Let an elastic spring of negligible small mass with its one end attached to a rigid support. Its other end is attached to a block of mass m which can slide over a smooth horizontal surface. The position x=0 is the equilibrium position. When the spring is stretched or compressed by pulling or pushing the block, the spring force Fs begins to act in the spring towards the equilibrium position.
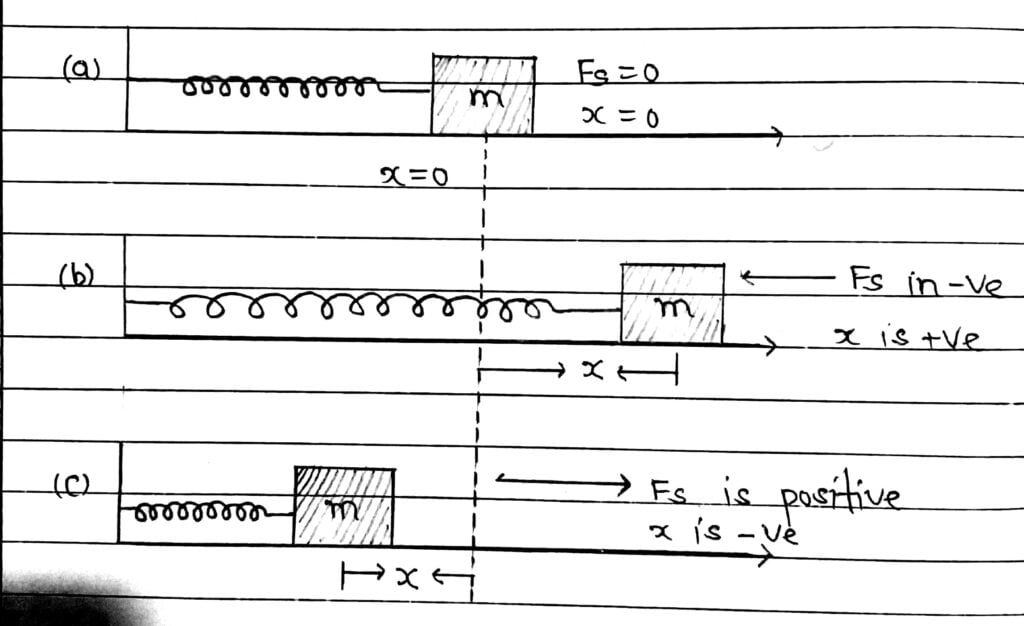
According to Hooke’s law the spring force Fs is proportional to the displacement of the block from the equilibrium position

Its SI unit is the N/m. The negative sign shows Fs acts in the opposite direction of x. The work done by the spring Force for a small extension dx is
dWs = Fs.dx = -kx.dx [Fs = -kx]

Conclusion
1. The spring force is position dependent.
2. The work done by the spring force depends on initial and final position.
3. The work done by the spring force in a cyclic process is zero.
Thus, spring force is a conservative force.
NCERT Class 11 Physics Book PDF Free Download
Also Read
SL Arora Class 11 Physics Book PDF Free Download
All In One Arihant Class 11 Physics Book PDF Free Download
Arihant All In One Chemistry Class 11 Book PDF Free Download
NCERT Class 11 Physics Hand Written Notes Chapter-Wise
Chapter-1 (Physical World) PDF Free Download
Chapter-2 (Units and Measurement) PDF Free Download
Chapter-3 (Motion In A Straight Line) PDF Free Download
Chapter-4 (Motion In A Plane) PDF Free Download
