Radioactivity:
A French physicist H Bequerel discovered radioactivity in 1896 by accident. Radioactivity is spontaneous nuclear phenomenon in which an unstable nucleus undergoes a decay with the emission of same(α,β) and electromagnetic radiations (γ) rays.
In nature, three types of radioactive decay occurs which are as-
α-Decay:
In α decay, a helium nucleus ₂He⁴ is emitted.
β-Decay:
In β decay, electrons or protons with the same mass as electron are emitted.
γ-Decay:
In γ decay, high energy≈100 KeV photons are emitted.
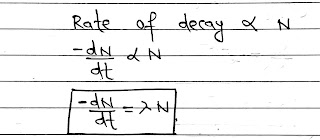
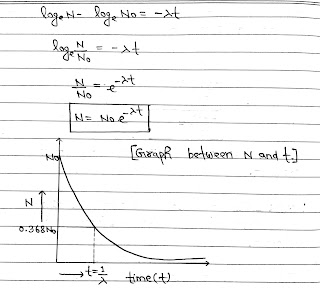
Law of Radioactive Decay:
Rutherford and soddy made experimental study of the radioactive decay of various radioactive materials and found that the decay of all radioactive materials is governed by the same general rule.
According to this law, the rate of decay of radioactive atoms at any instant is proportional to the number of atoms present at that instant.
let N be the number of atoms present in a radioactive substance at any instant t, then
Where amdus is called disintegration/Decay or Radioactive constant.