Let two body A and B of masses m₁ and m₂ kept on the x-axis. Initially the object B is at rest and A moves toward B with a speed u₁. If the collision is not head on, the object moves along different lines.
Let the object A moves with velocity v₁ making an angle θ with the x-axis and the object B moves with a velocity v₂ making an angle Ø with the same axis.
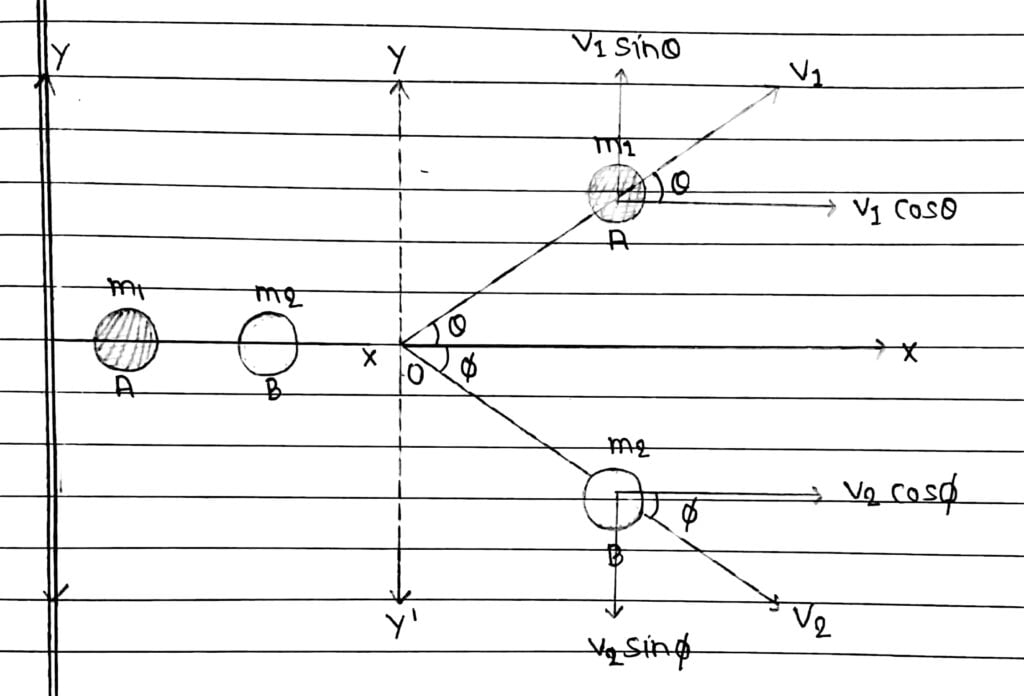
Let v₁ and v₂ lie in xy-plane, then by using conservation of angular momentum in x and y direction, we get
In X-Direction
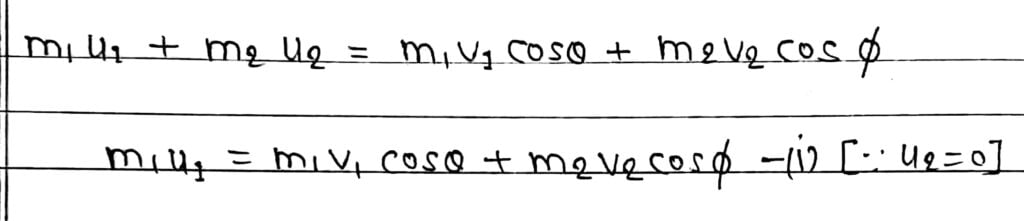
In Y-Direction
Initial momentum in y direction is zero, So

The four unknown quantities cannot be calculated by using the three equation, So if we calculate θ experimentally the value of other three unknown can be solved.
Now, The three casses can be considered as
Case-I:- Glancing Collision
In glancing collision, the incident partical does not lose any kinetic energy and is scattered almost undeflected. Thus for each collision θ is nearly equal to zero and Ø=90, then from equation (I) and (II), we get
u₁ = v₁ and v₂ = 0
Kinetic Energy of target particle = 1/2*m₂v₂² = 0
Case-II:- Head-On Collision
In this type of Collision, the target particle moves in the direction of the incident particle i.e Ø = 0, then from equation (I) and (II) becomes
m₁u₁ =m₁v₁cosθ + m₂v₂ and
0 = m₁v₁sinθ
From equation (III) the Kinetic Energy remains unchanged.
Case-III:- Elastic Collision Of Two Identical Particles
In this case,


Hence, We conclude that in a perfectly elastic collision, when a moving particle of mass m colloids elastically in two dimensions with another particle of mass m, after collision the two particle will move at right angle to each other.
NCERT Class 11 Physics Book PDF Free Download
Also Read
SL Arora Class 11 Physics Book PDF Free Download
All In One Arihant Class 11 Physics Book PDF Free Download
Arihant All In One Chemistry Class 11 Book PDF Free Download
NCERT Class 11 Physics Hand Written Notes Chapter-Wise
Chapter-1 (Physical World) PDF Free Download
Chapter-2 (Units and Measurement) PDF Free Download
Chapter-3 (Motion In A Straight Line) PDF Free Download
Chapter-4 (Motion In A Plane) PDF Free Download
