When an object follows a circular path at a constant speed, the motion of the object is called uniform circular motion. Although the speed does not very, the particle is accelerating because the velocity changes its direction at every point on the circular track.
Example:- Motion of the tip of the second hand of the clock.
Terms Related To Circular Motion
Angular Displacement
It is defined as the angle traced out by the radius vector at the centre of the circular path in the given time. It is denoted by ∆θ and expressed in radian.
It is a dimensionless quantity. It is a vector quantity.
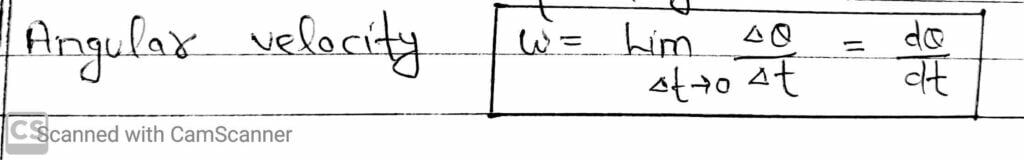
Angular Velocity
It is define as the time rate of change of its angular position.
It is denoted by ω and is measured in radian per second. It’s dimensional formula is [M⁰L⁰T⁻¹]. It is a vector quantity.
Time Period
It is defined as the time taken by a particle to complete an revolution along its circular path.
It is denoted by T and measured in second.
Frequency
It is defined as the number of revolutions completed per unit time.
It is denoted by f and measured in Hertz (Hz).
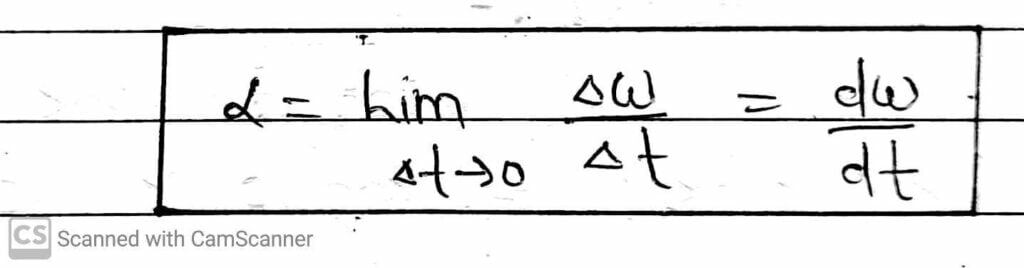
Angular Acceleration
It is define as the time rate of change of angular velocity of a particle.
It is measured in radian per second square and has dimension [M⁰L⁰T⁻²]. It is denoted by α.
NCERT Class 11 Physics Book PDF Free Download
Also Read
SL Arora Class 11 Physics Book PDF Free Download
All In One Arihant Class 11 Physics Book PDF Free Download
Arihant All In One Chemistry Class 11 Book PDF Free Download
NCERT Class 11 Physics Hand Written Notes Chapter-Wise
Chapter-1(Physical World) PDF Free Download
Chapter-2(Units and Measurement) PDF Free Download
