When we multiply a vector A by a real number λ, then we get a new vector along the direction of vector A. Its magnitude becomes λ times the magnitude of the given vector.
Similarly, if we multiply a vector A by a real number -λ, then we get a new vector whose magnitude is λ times the magnitude of the vector A but direction is opposite to that of vector A.
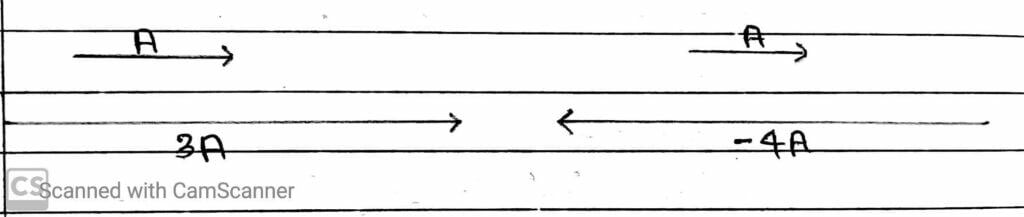
Example:- Consider a vector A is multiplied by a real number λ = 3 and λ = -4
Resultant Vector
The resultant vector of two or more vectors is defined as the single vector which produces the same effect as two or more vectors combinely produces.
Case-I: When two vectors are acting in the same direction
Let the vector A and B are acting in the same direction.

The resultant of this two vectors is given by a vector having direction as same of A or B and the magnitude of the resultant vector will be equal to the sum of the respective vectors.
Thus, the resultant vector R = A+B

Case-II: When two vectors are acting in mutually opposite directions.
Let vector A and B are acting in mutually opposite direction.

Then, the resultant of these two vectors is given by a vector having direction same as that of vector with larger magnitude. The magnitude of resultant vector will be equal to |A-B|.
Thus, the resultant vector R = A-B
If B>A, then direction of R is along B.
If A>B, then the direction of R is along A.
NCERT Class 11 Physics Book PDF Free Download
Also Read
SL Arora Class 11 Physics Book PDF Free Download
All In One Arihant Class 11 Physics Book PDF Free Download
Arihant All In One Chemistry Class 11 Book PDF Free Download
NCERT Class 11 Physics Hand Written Notes Chapter-Wise
Chapter-1(Physical World) PDF Free Download
Chapter-2(Units and Measurement) PDF Free Download
